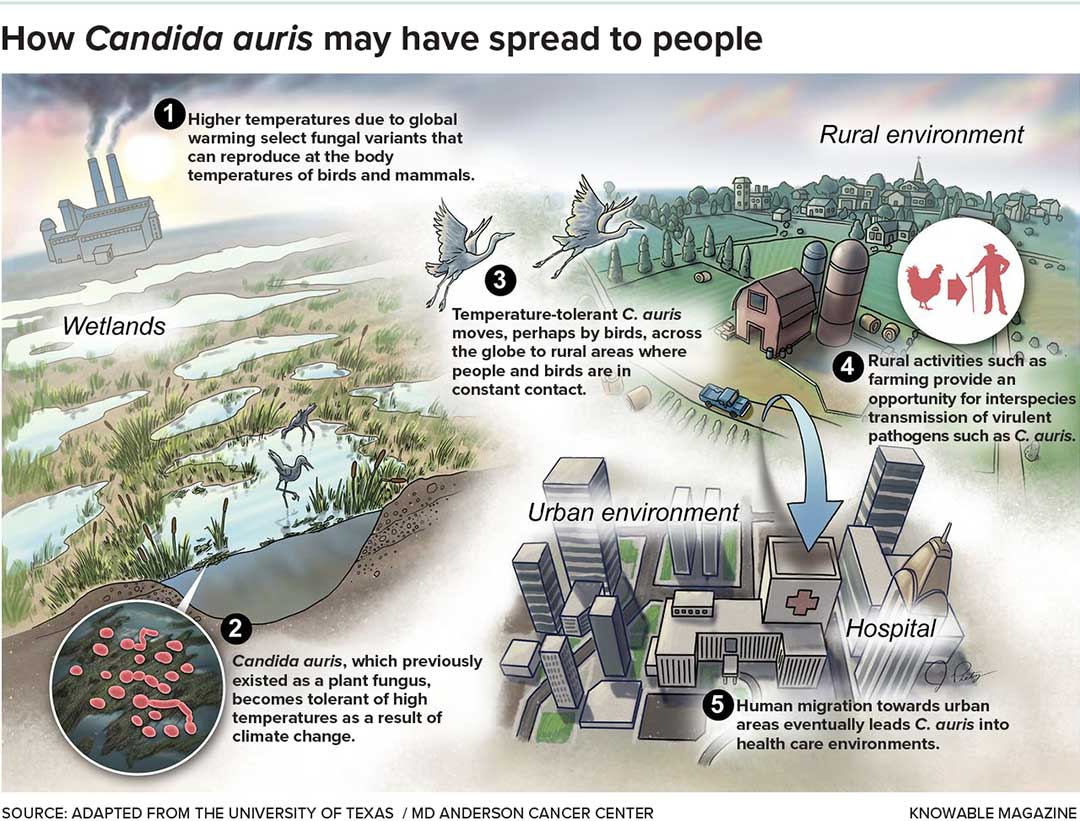
New research warns that rising global temperatures due to climate change will significantly expand the reach of dangerous fungal pathogens, particularly affecting the Aspergillus family. Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus, linked to severe diseases like aspergillosis and liver damage, could spread to 77% and 16% more territory respectively by 2100. This expansion, particularly into northern Europe, Asia, and the Americas, could expose millions more to infections. Fungi pose a distinct threat due to their hard-to-detect spores, drug resistance, and the lack of effective treatments. The World Health Organization has identified A. fumigatus as one of the most critical fungal threats. Climate factors like drought and wildfires are expected to exacerbate fungal spread, while structural inequalities may heighten risks for vulnerable populations, including rural and Latino communities. Fungal infections currently account for 3.8 million deaths annually, with 2.5 million being directly attributed to fungal pathogens. The lack of financial incentive has also impeded the development of anti-fungal drugs. Experts emphasize the urgent need for broader awareness, better diagnostic tools, and targeted medical research to mitigate this growing public health crisis.
Climate Change Fuels Spread of Deadly Fungal Pathogens


0 Comments